Alpine Catchments’ Hazard Related to Subaerial Sediment Gravity Flows Estimated on Dominant Lithology and Outcropping Bedrock Percentage
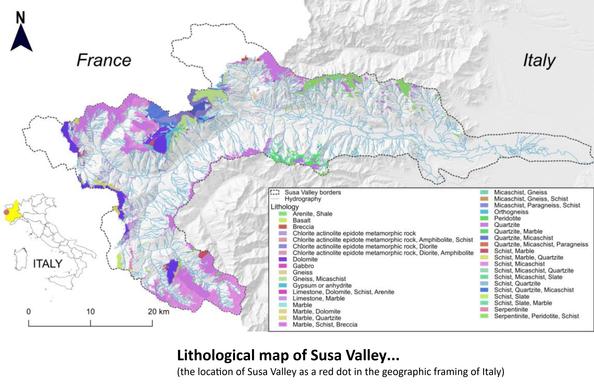
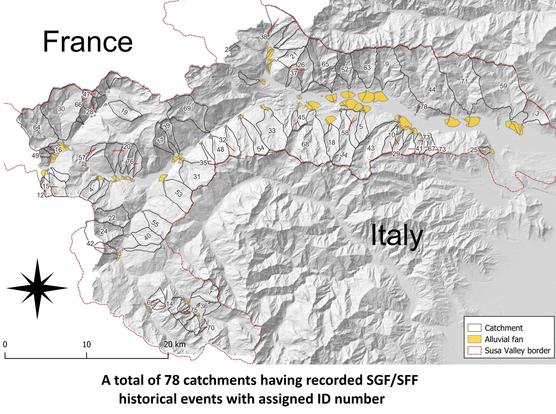
Sediment gravity flows (SGFs) cause serious damage in the Alpine regions. In the literature, several methodologies have been elaborated to define the main features of these phenomena, mainly considering the rheological features of the flow processes by laboratory experiments or by flow simulation using 2D or 3D propagation models or considering a single aspect, such as the morphometric parameters of catchments in which SGFs occur. These very targeted approaches are primarily linked to the definition of SGFs’ propagation behavior or to identify the predisposing role played by just one feature of catchments neglecting other complementary aspects regarding phenomena and the environment in which SGFs can occur. Although the research aimed at the quantification of some parameters that drive the behavior of SGFs provides good results in understanding the flow mechanisms, it does not provide an exhaustive understanding of the overall nature of these phenomena, including their trigger conditions and a complete view of predisposing factors that contribute to their generation. This paper presents a research work based on the collection and cross-analysis of lithological, geomechanical, geomorphological and morphometrical characteristics of Alpine catchments compared with sedimentological and morphological features of SGF deposits, also taking in to account the rainfall data correlation with historical SGF events. A multidisciplinary approach was implemented, aiming at quantifying SGF causes and characteristics starting from the catchments’ features where the phenomena originate in a more exhaustive way. The study used 78 well-documented catchments of Susa Valley (Western Italian Alps), having 614 historical flow events reported, that present a great variability in geomorphological and geological features. As the main result, three catchment groups were recognized based on the dominant catchment bedrock’s lithology characteristics that influence the SGFs’ rheology, sedimentological and depositional features, triggering rainfall values, seasonality, occurrence frequency and alluvial fan architecture. The classification method was also compared with the catchments’ morphometry classification, demonstrating that the fundamental role in determining the type of flow process that can most likely occur in a given catchment is played by the bedrock outcropping percentage, regardless of the results provided by the morphometric approach. The analysis of SGF events through the proposed method led to a relative estimate of the hazard degree of these phenomena distinguished by catchment type.