#Biotech #Alzheimers #DrugDelivery #Neuroscience #TechNews
#Biotech #Alzheimers #DrugDelivery #Neuroscience #TechNews
Nhà khoa học trẻ TP.HCM phát triển vật liệu nano dẫn truyền thuốc trúng đích, hứa hẹn mở ra hướng mới trong điều trị ung thư. #nanotechnology #cancerresearch #TPHCM #khoahọc #y học #đột phá
#materials #science #research #oncology #innovation #Vietnam #HCMC #nanomaterials #drugdelivery #targetedtherapy
Microneedles that could revolutionize cancer immunotherapy.
Made from natural polysaccharides, the new microneedles not only deliver drugs but also activate the immune system, paving the way for more effective and less invasive anticancer therapies.
Read more: https://omniletters.com/microneedles-that-could-revolutionize-cancer-immunotherapy/
#CancerImmunotherapy #Microneedles #Immunotherapy #CancerResearch #Oncology #DrugDelivery #TransdermalDelivery #Biomaterials #Polysaccharides #Nanomedicine #science #cancer
MIT just took a swing at one of the most annoying parts of modern medicine: hours‑long IV antibody infusions.
Their team figured out how to pack antibodies into tiny solid particles—about 100 microns wide—that stay suspended in liquid at ~360 mg/mL. That’s concentrated enough to deliver a full dose in about 2 mL, i.e., a normal subcutaneous injection, not a 100 mL drip.
https://mit-ki.org/4aHnV27
#Biotech #Oncology #DrugDelivery #MIT

A new way to deliver antibodies could make treatment much easier for patients
MIT engineers discovered a way to make solid particles of highly concentrated antibodies, suspended in a solution. The advance represents a major step toward re-formulating antibodies so that they can be injected using a standard syringe.
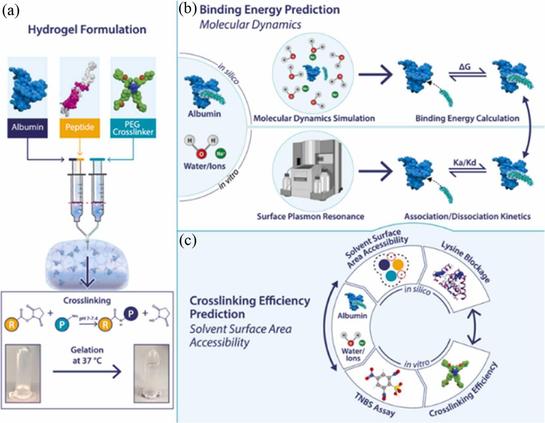
🧬 Can molecular simulations transform the future of long-acting diabetes treatments?
🔗 In silico investigations of albumin-GLP-1 receptor agonist complexes for diabetes drug delivery applications. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2025.11.007
📚 CSBJ: https://www.csbj.org/
#MolecularDynamics #DiabetesResearch #Biotherapeutics #GLP1 #Albumin #DrugDelivery #Biomaterials #ComputationalBiology #ProteinEngineering
Key highlights:
⚗️ Developed anionic and cationic agarose derivatives with tuneable degrees of substitution.
💧 Integrated these materials into hydrogels and alginate micro beads to enhance drug delivery performance.
⏱️ Achieved sustained and low-burst drug release over up to 14 days with advanced kinetic modelling for accurate release characterisation.
This research contributes to the development of biocompatible and efficient drug delivery systems with customisable release profiles. It now marks an end of this part of journey, where I have learned so much!
🔗 Read more: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.124622
#ControlledRelease #DrugDelivery #Biomaterials #AgaroseDerivatives #Hydrogels #Chemistry #Polysaccharides #Science
Carnegie Mellon University scientists have engineered microscopic robots, called AggreBots, using human lung cells. These bio-robots move with cilia, the tiny hairlike structures that naturally propel particles in the lungs. Researchers demonstrated for the first time that cilia-driven biological robots can be guided with precision. Published in Science Advances, this work opens new possibilities for targeted drug delivery, minimally invasive therapies, and future biomedical innovations. The approach shows how human cells can be re-engineered into active therapeutic tools, advancing the next generation of medical treatments.
Core discovery & science
#MedicalBreakthrough #BioRobotics #LifeSciences #FutureOfMedicine #ScienceAdvances
Technology & innovation
#AggreBots #CellEngineering #TargetedTherapy #DrugDelivery #MinimallyInvasive #Biotech
Impact & applications
#InnovativeMedicine #NextGenHealthcare #CuttingEdgeScience #BiomedicalEngineering #HealthTech
🔗 https://av.tib.eu/media/71586
#DrugDelivery #vaccines #GlobalHealth #CancerImmunotherapy #BeilsteinTalks
🔗 https://av.tib.eu/media/71537
#DrugDelivery #siRNA
#BeilsteinTalks