in the #arXiv
J1721+8842: The first Einstein zig-zag lens
by Frédéric Dux and co-authors
https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.04177
#Cosmology #galaxies #quasars #lensing #astronomy #astrophysics #astrodon #JWST #Webb #telescope #space #science #STEM
J1721+8842: The first Einstein zig-zag lens
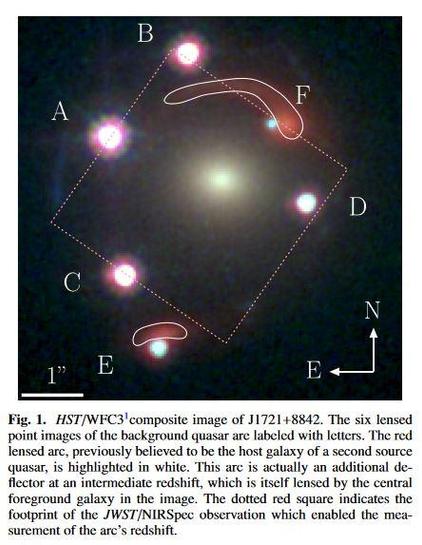
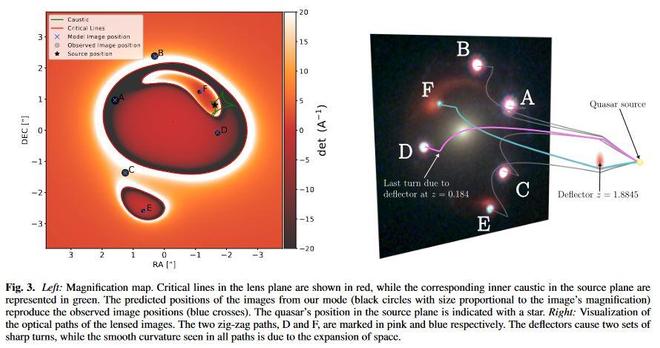
We report the discovery of the first example of an Einstein zig-zag lens, an extremely rare lensing configuration. In this system, J1721+8842, six images of the same background quasar are formed by two intervening galaxies, one at redshift $z_1 = 0.184$ and a second one at $z_2 = 1.885$. Two out of the six multiple images are deflected in opposite directions as they pass the first lens galaxy on one side, and the second on the other side -- the optical paths forming zig-zags between the two deflectors. In this letter, we demonstrate that J1721+8842, previously thought to be a lensed dual quasar, is in fact a compound lens with the more distant lens galaxy also being distorted as an arc by the foreground galaxy. Evidence supporting this unusual lensing scenario includes: 1- identical light curves in all six lensed quasar images obtained from two years of monitoring at the Nordic Optical Telescope; 2- detection of the additional deflector at redshift $z_2 = 1.885$ in JWST/NIRSpec IFU data; and 3- a multiple-plane lens model reproducing the observed image positions. This unique configuration offers the opportunity to combine two major lensing cosmological probes: time-delay cosmography and dual source-plane lensing since J1721+8842 features multiple lensed sources forming two distinct Einstein radii of different sizes, one of which being a variable quasar. We expect tight constraints on the Hubble constant and the equation of state of dark energy by combining these two probes on the same system. The $z_2 = 1.885$ deflector, a quiescent galaxy, is also the highest-redshift strong galaxy-scale lens with a spectroscopic redshift measurement.