Overcoming Antibiotic Resistance to Tetracycline in Staphylococcus aureus by Gold and Silver Nanoparticles - Cytology and Genetics
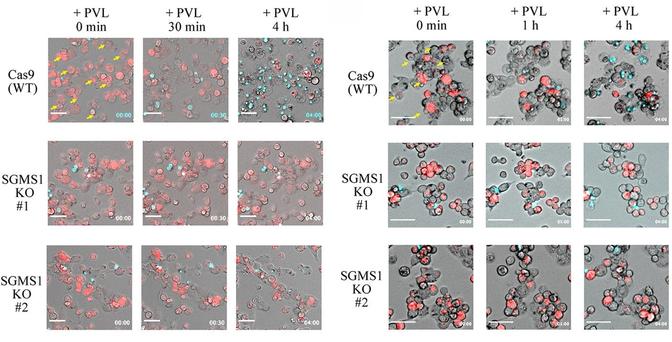
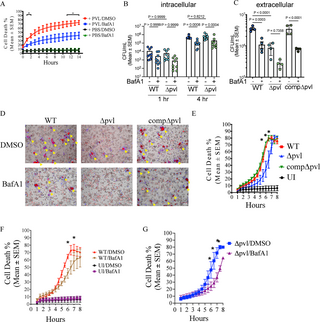
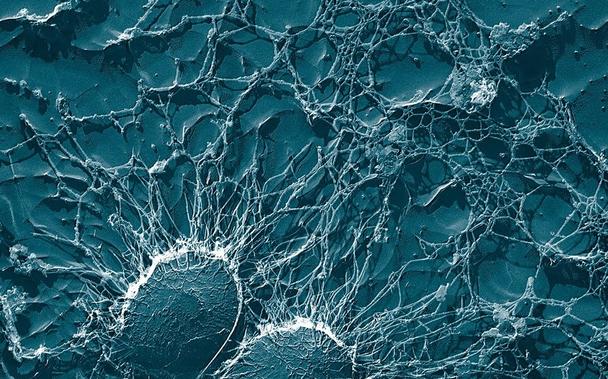
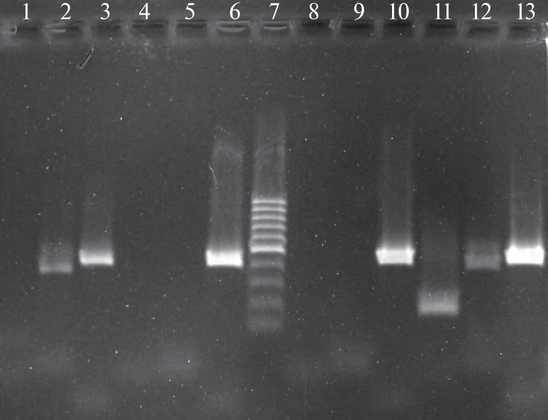
Abstract The use of tetracyclines in medicine, veterinary medicine, and stock raising has led to the spread of bacterial resistance to tetracycline, particularly among dangerous representatives of Staphylococcus aureus. Therefore, the analysis of resistance to tetracycline and the creation of approaches to overcome it are extremely relevant. Studies of 64 clinical isolates of S. aureus, which were characterized by moderate biofilm formation, showed that 33 of them contained plasmid DNA. A significant spread (in 96% of studied isolates) of the known transmissible tetracycline resistance genes tet(K) and tet(M) was shown in the examined plasmid-containing doxycycline-resistant clinical isolates of S. aureus. Plasmid-containing doxycycline-resistant clinical isolates with tet(K) and tet(M) genes lost resistance to the tetracycline antibiotic doxycycline after treatment of their cells with gold nanoparticles of 30 nm in a concentration of 3.2–9.6 μg/mL or medium-sized silver of 30 nm in a concentration of 20–40 μg/mL. Elimination of tet genes responsible for acquired resistance was confirmed by PCR.