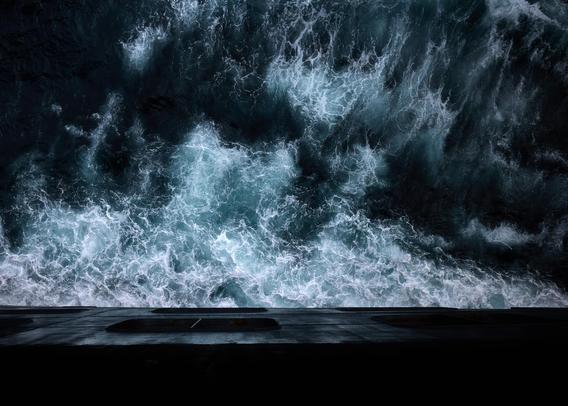
Image taken from Queen Mary 2 as it sails through the North Atlantic. The perspective highlights the stark contrast between the ship's structure. For me, the sea has a strange and deadly effect that invites to go in the water - perhaps like the sirens of mythology.
#queenmary2 #northatlantic #ship #travel #nature #voyage #water #photo #ocean #sea #atlantic #photography #cunard