#FYI via Prof. #EliotJacobson #climatecasino #Paris #France #heatwave
Your 'moment of doom' for Aug. 18, 2025 ~ Sooner than expected.
"Given updated decadal warming rates currently estimated to be in the region of 0.34C to 0.40C per decade, such 50C heat waves could even occur as soon as the late 2030s, 11 to 12 years earlier than 2050."
(article paywalled)
https://www.nytimes.com/2025/08/18/world/europe/france-heat-wave-paris-climate-change-planning.html
#ClimateEmergency #ClimateCrisis #ClimateBreakdown #ClimateDisruption #globalHeating #ExtremeWeather

As Heat Waves Intensify, Paris Plans for Record Temperatures
City planners say the day when temperatures as high as 122 degrees Fahrenheit, or 50 Celsius, could stall the French capital is not far off. They are already starting to prepare.
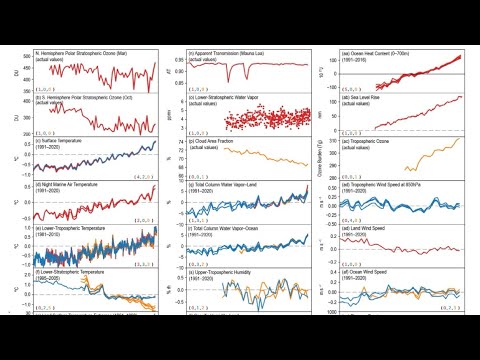
Climate Surprises and What You Probably Don’t Know about Climate; from “State of the Climate 2024”

Guns, Tanks, and Heatwaves: Rethinking Security in the Age of Climate Change – Erin Sikorsky

Plastics treaty talks collapse without a deal after "chaotic" negotiations
UN talks ran into overtime, ending with a standoff over whether a treaty should include curbs on plastic production and the way forward unclear

NEW Report: State of the Climate 2024: An Awesome, Detailed, Extensive, New, Peer-Reviewed Report
#microbes #icemelt #Greenland #glacier #algae
original open access article
Cook et al. 29 Jan 2020, Cryosphere 14(1):309–330
Glacier algae accelerate melt rates on the south-western Greenland Ice Sheet
"microbes there are responsible for 4.4 to 6.0 gigatons of runoff, representing up to 13% of total melt"
https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-14-309-2020
climate #ClimateScience #climatechange #ClimateEmergency #ClimateCrisis #ClimateBreakdown #ClimateDisruption #globalWarming #globalHeating #ExtremeWeather
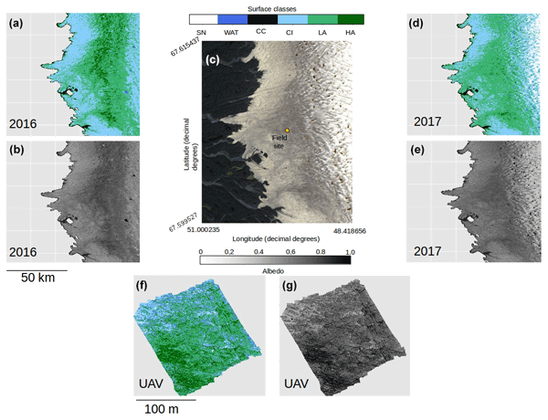
Glacier algae accelerate melt rates on the south-western Greenland Ice Sheet
Abstract. Melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet (GrIS) is the largest
single contributor to eustatic sea level and is amplified by the growth
of pigmented algae on the ice surface, which increases solar radiation
absorption. This biological albedo-reducing effect and its impact upon sea
level rise has not previously been quantified. Here, we combine field
spectroscopy with a radiative-transfer model, supervised classification of
unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and satellite remote-sensing data, and runoff modelling to calculate
biologically driven ice surface ablation. We demonstrate that algal growth
led to an additional 4.4–6.0 Gt of runoff from bare ice in the
south-western sector of the GrIS in summer 2017, representing 10 %–13 %
of the total. In localized patches with high biomass accumulation, algae
accelerated melting by up to 26.15±3.77 % (standard error, SE). The year 2017
was a high-albedo year, so we also extended our analysis to the particularly low-albedo 2016 melt season. The runoff from the south-western bare-ice zone attributed to algae was much higher in 2016 at 8.8–12.2 Gt, although the
proportion of the total runoff contributed by algae was similar at 9 %–13 %. Across a 10 000 km2 area around our field site, algae covered
similar proportions of the exposed bare ice zone in both years (57.99 %
in 2016 and 58.89 % in 2017), but more of the algal ice was classed as
“high biomass” in 2016 (8.35 %) than 2017 (2.54 %). This interannual
comparison demonstrates a positive feedback where more widespread, higher-biomass algal blooms are expected to form in high-melt years where the
winter snowpack retreats further and earlier, providing a larger area for bloom
development and also enhancing the provision of nutrients and liquid water
liberated from melting ice. Our analysis confirms the importance of this
biological albedo feedback and that its omission from predictive models
leads to the systematic underestimation of Greenland's future sea level
contribution, especially because both the bare-ice zones available for algal
colonization and the length of the biological growth season are set to
expand in the future.
#FYI via Prof. #EliotJacobson
Your 'moment of doom' for Aug. 15, 2025 ~ Feedback loop alert!
"these factors have the potential to trigger an amplifying positive feedback loop: ice-darkening microbes nudge up temperatures and accelerate melt, exposing more nutrient-rich debris that encourage the growth of yet more microbes..."
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/aug/15/arctic-glaciers-face-terminal-decline-as-microbes-accelerate-ice-melt
climate #ClimateScience #climatechange #ClimateEmergency #ClimateCrisis #ClimateBreakdown #ClimateDisruption
Arctic glaciers face ‘terminal’ decline as microbes accelerate ice melt
Scientists in Svalbard in race to study polar microbes as global heating threatens fragile glacial ecosystems
Michael Mann on BBC Discussing Climate Change Impacts on Wildfires in North America (AUG 6 2025)







