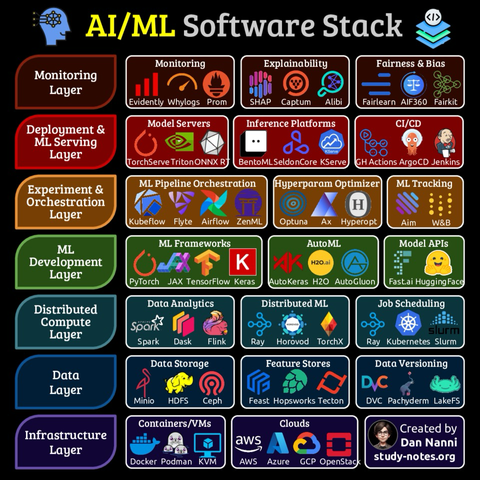
#Jenetics #GeneticAlgorithm #GeneticProgrammin #Cryptography #Security #SoftwareEngineering
https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.10323

ELFuzz: Efficient Input Generation via LLM-driven Synthesis Over Fuzzer Space
Generation-based fuzzing produces appropriate testing cases according to specifications of input grammars and semantic constraints to test systems and software. However, these specifications require significant manual efforts to construct. This paper proposes a new approach, ELFuzz (Evolution Through Large Language Models for Fuzzing), that automatically synthesizes generation-based fuzzers tailored to a system under test (SUT) via LLM-driven synthesis over fuzzer space. At a high level, it starts with minimal seed fuzzers and propels the synthesis by fully automated LLM-driven evolution with coverage guidance. Compared to previous approaches, ELFuzz can 1) seamlessly scale to SUTs of real-world sizes -- up to 1,791,104 lines of code in our evaluation -- and 2) synthesize efficient fuzzers that catch interesting grammatical structures and semantic constraints in a human-understandable way. Our evaluation compared ELFuzz with specifications manually written by domain experts and synthesized by state-of-the-art approaches. It shows that ELFuzz achieves up to 434.8% more coverage and triggers up to 174.0% more artificially injected bugs. We also used ELFuzz to conduct a real-world fuzzing campaign on the newest version of cvc5 for 14 days, and encouragingly, it found five 0-day bugs (three are exploitable). Moreover, we conducted an ablation study, which shows that the fuzzer space model, the key component of ELFuzz, contributes the most (up to 62.5%) to the effectiveness of ELFuzz. Further analysis of the fuzzers synthesized by ELFuzz confirms that they catch interesting grammatical structures and semantic constraints in a human-understandable way. The results present the promising potential of ELFuzz for more automated, efficient, and extensible input generation for fuzzing.