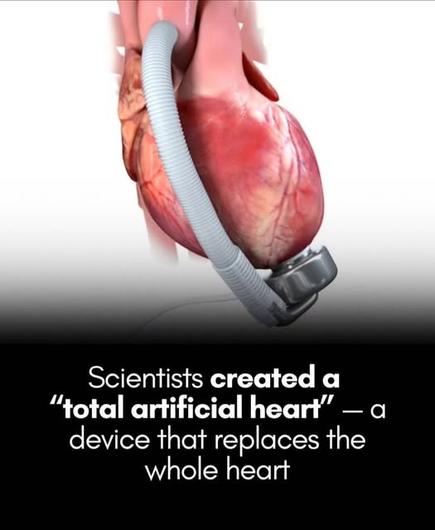
A French company has created a total artificial heart.
A French medical tech company, Carmat, has developed a groundbreaking "total artificial heart" that mimics the body’s natural rhythms by adjusting blood flow in real time based on the patient’s activity level.
Weighing 4 kilograms and powered by battery packs, the device uses sensors and an onboard algorithm to detect blood pressure and regulate circulation—ramping up flow during physical exertion and easing it at rest.
Designed with biocompatible materials to reduce complications, the artificial heart functions as a bridge to transplant for patients with end-stage heart failure, offering hope amid donor shortages. Yes, this means that is can function as the whole heart.
However, it is not meant to work for the rest of the patients life. But act as a stop-gap until a donor can be found.
Now approved for sale in the EU, Carmat’s heart is set to launch in Germany and is priced at over €160,000.
Though currently too large for most women, the company aims to refine its design. Meanwhile, another French company, CorWave, is developing a responsive blood-pumping device for patients with less severe heart failure. Both technologies are steps toward a future where mechanical hearts may become permanent, life-sustaining alternatives to human transplants—especially as developers gather long-term data to prove their safety and reliability.
Reference: Bailey, S. "This new artificial heart responds to the patient." CNN Business, March 25.
Core discovery & medical tech
#MedicalBreakthrough #Cardiology #ArtificialHeart #LifeSciences #FutureOfMedicine
Device & innovation
#Carmat #HeartTechnology #MedicalDevices #Biotech #HealthTech #MechanicalHeart
Impact & patient care
#EndStageHeartFailure #OrganShortageSolutions #BridgeToTransplant #InnovativeMedicine #NextGenHealthcare