#Ottoman-#Pharaonic Truce shifts #Egypt-#Turkey rivalry to the #HornOfAfrica. Tactical alignment redirects resources, altering regional #Geopolitics. Key issues: Sharm el-Sheikh's impact, #Houthi-#AlShabaab collaboration, & #Ethiopia-#Somaliland relations.
https://saxafimedia.com/ottoman-pharaonic-truce-sharm-el-sheikh-horn/

The Ottoman–Pharaonic Truce: How Sharm El-Sheikh Redirects Conflict To The Horn | Saxafi Media
In the shifting sands of Middle Eastern geopolitics, old rivalries do not die they evolve. For over a decade, Turkey under Recep Tayyip Erdogan has pursued a Neo-Ottoman vision, seeking to reclaim influence in lands once under Ottoman sway, from the Levant and North Africa to the distant Horn of Africa. This approach blends Islamism with proxy support and bold maritime expansions, extending soft power through aid, military bases, and economic footholds in places like Somalia and Libya.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-21784-y
#EyeHealth #VisionCare #PublicHealth #Ethiopia
Top causes of visual impairment, satisfaction with eye care services, and associated factors among visually impaired patients attending an eye care center in Ethiopia - Scientific Reports
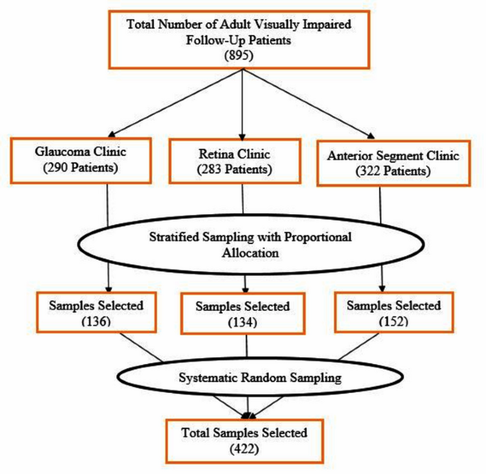
Due to limited access to timely and affordable eye care, the burden of visual impairment is disproportionately high in low- and middle-income countries, including Ethiopia. However, the quality of eye care services and patients’ satisfaction with these services among visually impaired individuals has not been adequately studied. This study aimed to assess the main causes of visual impairment, satisfaction with eye care services, and identify associated factors among visually impaired follow-up patients attending Hawassa University Comprehensive Specialized Hospital–Eye Care and Training Center (HUCSH-ECTC), Southern Ethiopia, 2024. An institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted from June 22 to August 2, 2024, on adult visually impaired follow-up patients using a stratified sampling technique. Data were collected through medical chart reviews and pre-tested, structured interviewer-administered questionnaires. The data were analyzed using Stata version 17. Binary logistic regression analysis was performed, and variables with a p value of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Four hundred fourteen (98.1% response rate) adult visually impaired follow-up patients were included in this study. Cataract, uncorrected refractive error, and glaucoma were found to be the top three causes of visual impairment. The prevalence of satisfaction was 43.0% (95% CI 38.3–47.8). Health insurance (AOR 2.06, (95% CI 1.24–3.43)), substance use (AOR 2.95, (95% CI 1.35–6.45)), mild and moderate level visual impairment (AOR 2.94, (95% CI 1.47–5.89)), and systemic comorbidity (AOR 4.22, (95% CI 2.41–7.40)) were significant factors associated with satisfaction. The top three causes of visual impairment were cataract, uncorrected refractive error, and glaucoma. Relatively lower eye care service-related satisfaction was observed among adult visually impaired follow-up patients attending the HUCSH-ECTC, Southern Ethiopia. The significant factors affecting satisfaction were valid health insurance, current substance use, visual impairment level, and systemic comorbidity occurrence. For visual impairment patients visiting eye care centers, better treatment, assistance, and targeted rehabilitation services are suggested.



