The Hidden Cost of API Security Misconfigurations (and How to Avoid Them)
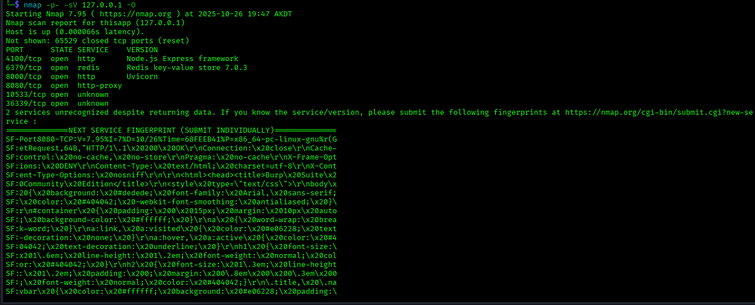
This article comprehensively covers **OWASP API8:2023 Security Misconfiguration** vulnerabilities, which encompass multiple attack vectors stemming from improper API security controls. Security misconfigurations represent a class of vulnerabilities where insecure default settings, incomplete configuration of security controls, or exposure of unnecessary features create exploitable attack surfaces. The vulnerability manifests through various attack vectors including default credentials, verbose error messaging that reveals system information, enabled debugging modes, misconfigured cloud storage, weak TLS/SSL configurations, missing security headers, overly permissive CORS policies, unpatched software, and exposed internal endpoints. A practical exploitation example is demonstrated using the C{api}tal vulnerable application where an attacker discovered an exposed Redis instance running on port 6379 with no authentication. The exploitation involved simple reconnaissance using `nmap` to identify running services, followed by connecting to the unsecured Redis instance using `redis-cli` and extracting sensitive data including a security flag through basic commands like `keys *` and `get flag`. The impact spans multiple dimensions: unauthorized data access, potential system compromise through exposed sensitive information, MITM attacks via weak encryption, cross-site data leaks through permissive CORS, and reconnaissance opportunities provided by verbose error messages. The root causes include failure to implement secure defaults, lack of proper access controls, inadequate input validation, missing security headers, improper error handling, and insufficient security testing during deployment. Mitigation requires implementing secure default configurations by changing all default credentials, hardening environments through repeatable processes, enforcing least privilege principles, minimizing information leakage through generic error handling, establishing patch management policies, deploying automated security audits and monitoring, integrating security validation into CI/CD pipelines, implementing strong authentication/authorization mechanisms like OAuth 2.0 and MFA, and maintaining comprehensive API documentation. The vulnerability is particularly dangerous because it represents a category of weaknesses rather than a single flaw, making comprehensive security controls essential rather than point solutions. Organizations must prioritize robust quality assurance and security testing throughout the development lifecycle to prevent these easily preventable but often critical security gaps.
#infosec #BugBounty #APISecurity #SecurityMisconfiguration #Cybersecurityhttps://medium.com/@jungoskillet/security-misconfigurations-f132701315fd?source=rss------bug_bounty-5