𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗼𝗻𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 𝗼𝗳 𝗮 𝗥𝗮𝗱𝗶𝗼 𝗧𝗲𝗹𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗼𝗽𝗲 𝗥𝗲𝗰𝗲𝗶𝘃𝗲𝗿: An Overview of Essential Terms
📦 The Receiver Box:
The entire receiver system is housed in an interchangeable receiver box, which allows for quick and easy swapping of receivers.
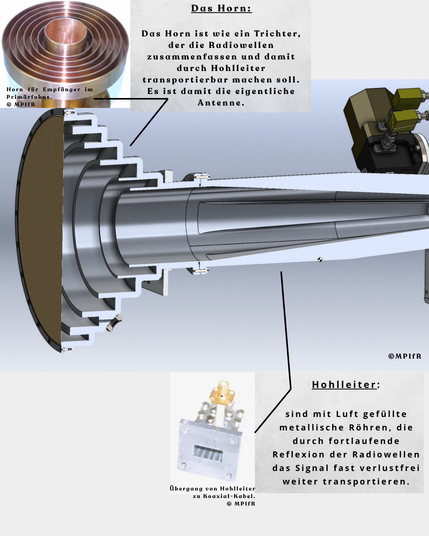
📡 The Horn:
The horn acts like a funnel that collects incoming radio waves and concentrates them so they can be transported via waveguides. It effectively serves as the actual antenna.
🔗 Waveguides:
These are air-filled metallic tubes that transmit the radio signal with minimal loss by guiding the waves through continuous internal reflection.
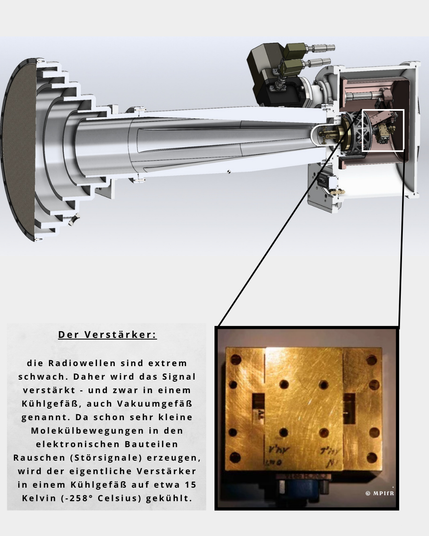
❄️ The Amplifier:
Radio waves are extremely weak when received, so the signal needs to be amplified. This amplification takes place inside a cryogenic vessel, also known as a vacuum chamber. Because even minimal molecular motion within the electronic components can create noise (unwanted signals), the amplifier itself is cooled down to around 15 Kelvin (-258° Celsius) to minimize interference.