The key to #effectiveModeling is to simplify a complex shape into elementary components. Sometimes, this involves mentally flattening and reducing 3D shapes to 2D shapes, extracting elementary curves from them, and then recreating the 3D shapes from the extracted 2D curves.
This is not always easy for organic shapes (which can still be approximated by Bézier curves). I extracted the #primaryCurves for the #IonicScroll surface in https://pixelfed.social/p/Splines/789956327130679640 after a lengthy trial-and-error process that involved #curveFitting images from #Vignola’s book, #RegolaArchitettura. I had to #reverseEngineer the details because the measurements have either been lost, or are locked away in some library. Web search yields no details on these measurements.
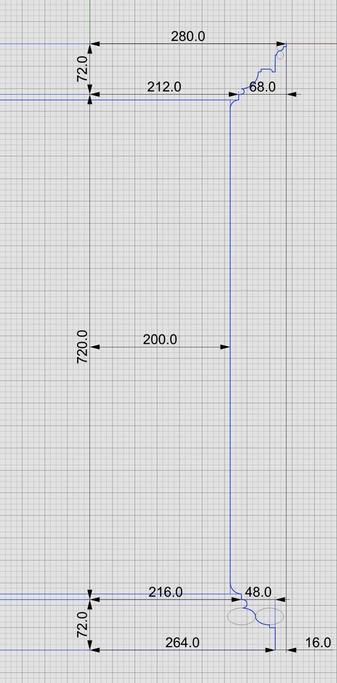
Fortunately, for geometrical shapes like pedestals, this is very easy. Because of its square footprint, mentally slicing it through the middle from top to bottom, it is easy to “see” the outline. Another way to think about #curveExtraction is to shine an imaginary bright light on an object from behind in a dark room to reveal its silhouette.
For the pedestal, even this silhouette or outline can be further reduced because the shape is symmetrical about the #columnAxis. With this realization, we only need to focus on one half of the outline, and methodically proceed from bottom to top, marking every kink and inflection point on the outline.
Fortunately, the other authoritative book, #Scarlata’s #PracticalArchitecture, I mentioned in my introductory post already documents #VignolaProportions in tabular form. So we can skip everything else and go directly to that.
Total height of #IonicPedestal is 864 units (108 parts, or 6*µ) of which the #PedestalBasement and #PedestalCap are each 72 units (9 parts, or µ/2) and the #Dado is 720 units (90 parts, or µ*5) tall.
Splines (@Splines@pixelfed.social)
This sweeping shape is a timeless design that first appeared in the scrolls of the #IonicCapital as the most distinctive part of the #IonicOrder in classical Greco-Roman architecture more than 2500 years ago. Shown here with a zebra pattern on the wireframe of a CAD model to accentuate its features and attest to the smoothness of its 3-dimensional surface, the design has been refined many times since the original version over the last two millennia. The two most remarkable things about this design are that: — It can be recreated with modern CAD tools by drawing simple 2-dimensional straight lines and circular arcs exclusively. The end result is truly breathtaking and makes one wonder how architects visualized the result and put theory into practice. In the CAD model, the ultimate surface is a #NURBS surface that uses #BSplines extensively, but none of the B-splines or surfaces need to be created "by hand." One only has to draw straight lines and circular arcs with accurate measurements snapped to grids. — For a design that has survived the ages, it is lamentable how few authoritative sources that accurately describe fine details and exact reconstruction methodology remain accessible to the general public in the age of Internet. The most comprehensive is the 10-volume tome that Marcus #Vitruvius Pollio, a Roman architect and engineer, wrote for #JuliusCaesar and his successor Emperor #CaesarAugustus. [https://www.gutenberg.org/files/20239/20239-h/20239-h.htm] I frequently use two more authoritative sources: — "Regola delli cinque ordini d' architettura," or simply #RegolaArchitettura by Giacomo Barozzi da #Vignola [https://archive.org/details/gri_33125008229458/page/n3/mode/2up], and — "A Course in Theoretical and Practical Architecture," or simply #PracticalArchitecture by Francisco Salvatore #Scarlata (#Bordonaro), which documents #VignolaProportions in tabular form [https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015031201190&view=1up&seq=5]