https://shorturl.at/HJwKk
@awi F: Pixabay CC
#Mikroorganismen in der #Antarktis reagieren stark auf steigende Temperaturen und den Rückgang des #Meereises.
Wärmere Bedingungen verändern das Gleichgewicht zwischen #Bakterien und #Phytoplankton – mit möglichen Folgen für die gesamte marine #Nahrungskette.
Weniger #Phytoplankton bedeutet weniger #Nährstoffe für #Krill, #Fische und #Meeressäuger.
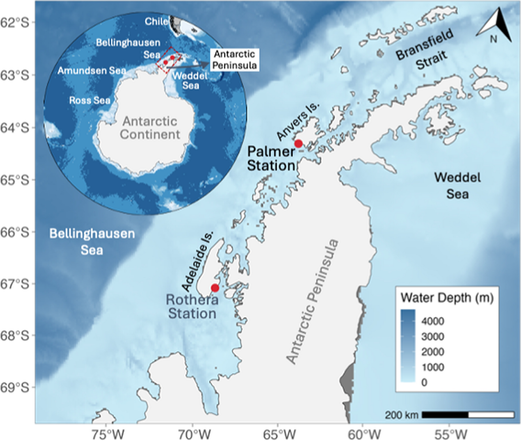
Background The west Antarctic Peninsula (WAP) is a region of rapid environmental changes, with regional differences in climate warming along the north–south axis of the peninsula. Along the WAP, Palmer corresponds to a warmer region with lesser sea ice extent in the north compared to Rothera ~ 400 km to the south. Comprehensive and comparative, year-round assessments of the WAP microbial community dynamics in coastal surface waters at these two locations are imperative to understand the effects of regional climate warming variations on microbial community dynamics, but this is still lacking. Results We report on the seasonal diversity, taxonomic overview, as well as predicted inter-and intra-domain causal effects (interactions) of the bacterial and microbial eukaryotic communities close to the Palmer station and at the Rothera time-series site between July 2013 and April 2014. Our 16S- and 18S-rRNA gene amplicon sequencing data showed that across all seasons, both bacteria and microbial eukaryotic communities were considerably different between the two sites which could be attributed to seawater temperature, and sea ice coverage in combination with sea ice type differences. Overall, in terms of biotic drivers, causal-effect modelling suggests that bacteria were stronger drivers of ecosystem dynamics at Palmer, while microbial eukaryotes played a stronger role at Rothera. The parasitic taxa Syndiniales persevered at both sites across the seasons, with Palmer and Rothera harbouring different key groups. Up to 62.3% of the negative causal effects were driven by Syndiniales at Rothera compared to only 13.5% at Palmer, suggesting that parasitism drives community dynamics at Rothera more strongly than at Palmer. Conversely, SAR11 Clade II, which was less abundant but persistent year-round at both sites, was the dominant driver at Palmer, evidenced by many (28.2% and 37.4% of positive and negative effects respectively) strong causal effects. Article note: Kindly check first page article notes are correct. Conclusions Our research has shed light on the dynamics of microbial community composition and correlative interactions at two sampling locations that represent different climate regimes along the WAP.
#Klimawandel zwingt #Eisbären zunehmend in die Nähe menschlicher Siedlungen, was zu gefährlichen Begegnungen führt. In Rankin Inlet, #Nunavut, kam es kürzlich zu einem tödlichen Angriff, als zwei Eisbären einen Radartechniker töteten. Experten warnen, dass die Veränderung des #Meereises die #Nahrungssuche der Bären stört und sie näher an menschliche Siedlungen treibt. Die Situation könnte sich verschärfen, bevor die #Bärenpopulationen langfristig zurückgehen.
Eine Studie der British Antarctic Survey zeigt, dass der Rückgang des #Meereises in der #Antarktis 2023 zu #Brutversagen bei einem Fünftel der #Kaiserpinguin-Kolonien führte. Wenn das Eis zu früh bricht, sterben junge #Pinguine, die noch nicht schwimmfähig sind. Langfristige Vorhersagen warnen, dass die Kaiserpinguin-Population bis Ende des Jahrhunderts um 99% fallen könnte, sollte der #Treibhausgasausstoß weiter steigen.
Es wird prognostiziert, dass eine zusätzliche Erwärmung das #Auftauen des #Permafrosts und den #Verlust der saisonalen #Schneedecke, des #Landeises und des arktischen #Meereises weiter verstärken wir. (#IPCC WGI AR6 2021)
Es wird prognostiziert, dass eine zusätzliche Erwärmung das #Auftauen des #Permafrosts und den #Verlust der saisonalen #Schneedecke, des #Landeises und des arktischen #Meereises weiter verstärken wir. (#IPCC WGI AR6 2021)