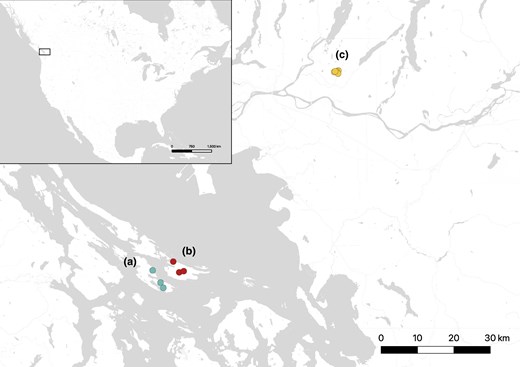
Howell et al. used WGS of wild-caught deer mice from two islands and one mainland location in British Columbia to investigate chromosomal inversions and non-equilibrium demographic history of this species.
Maclary & Shapiro used comparative genomics to examine coding variation in EDNRB2, a candidate gene for loss of plumage melanin across birds, finding widespread coding variation in EDNRB2 and other pigmentation genes with limited pleiotropy.
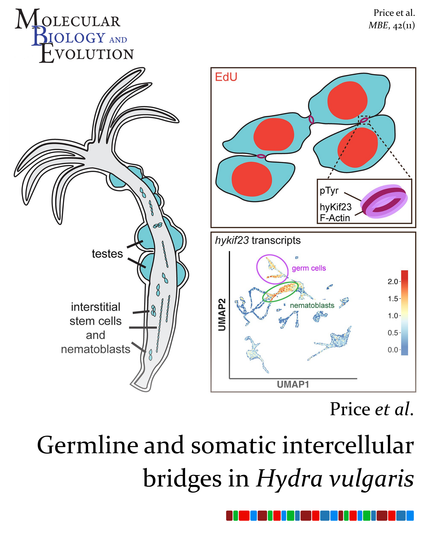
Price et al. characterized germline and somatic intercellular bridges in the cnidarian Hydra vulgaris, revealing that the molecular and structural features of intercellular bridges in Hydra are conserved across lineages.
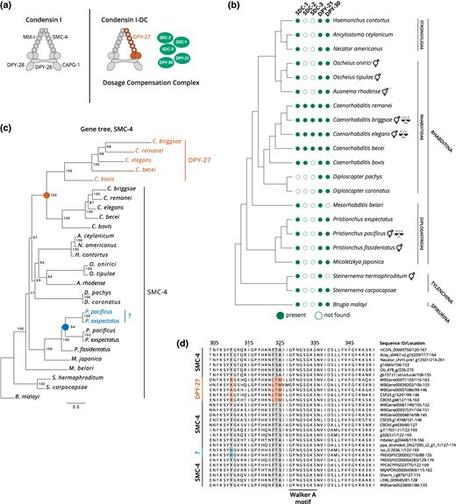
Aharonoff et al. show that dosage compensation mechanisms continue to evolve in species with shared X chromosome ancestry, and that the process of evolving chromosome-wide gene regulatory mechanisms is constrained.
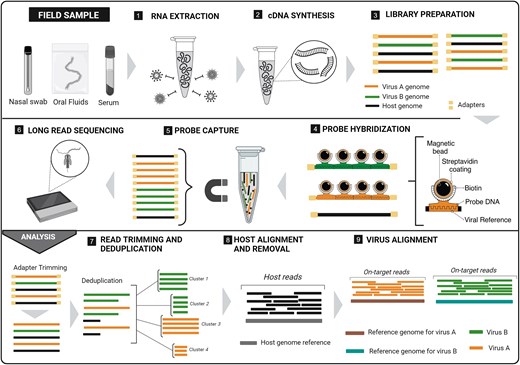
Meneguzzi et al. combined targeted enrichment with long-read, real-time sequencing to create the TELSVirus workflow for rapid detection and genomic characterization of multiple low-abundance viruses from single samples using long-read sequencing.
Roussel et al. characterized TE content in naturally occurring killifish hybrids, finding higher TE load and accumulation of Neptune subfamilies in hybrids.
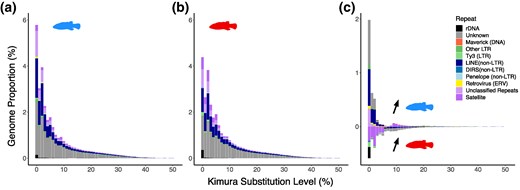
Accumulation of a Biparentally Inherited Neptune Transposable Element in Natural Killifish Hybrids (Fundulus diaphanus × F. heteroclitus)
Abstract. Transposable elements (TEs) are abundant selfish genetic elements that can mobilize in their host genome, causing DNA damage, mutations, and chro
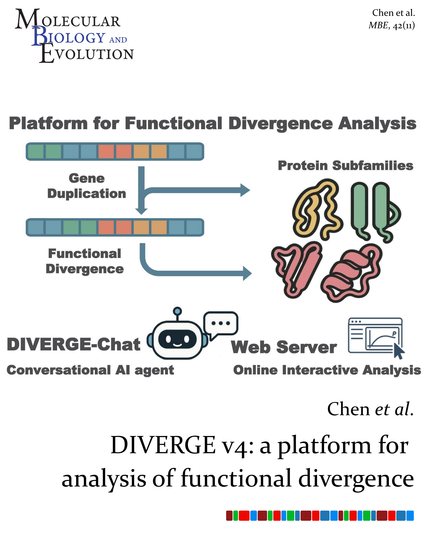
Chen et al. present the version 4 upgrade of the DIVERGE software for identifying amino acid residues critical to functional shifts between protein subfamilies, which includes DIVERGE-Chat, a conversational AI agent for intuitive, code-free exploration.
Zhang et al. present NeuralNJ, an accurate and efficient approach to phylogenetic inference whose innovation lies in its learnable neighbor joining mechanism, which iteratively joins neighbors guided by learned priority scores for tree reconstruction.
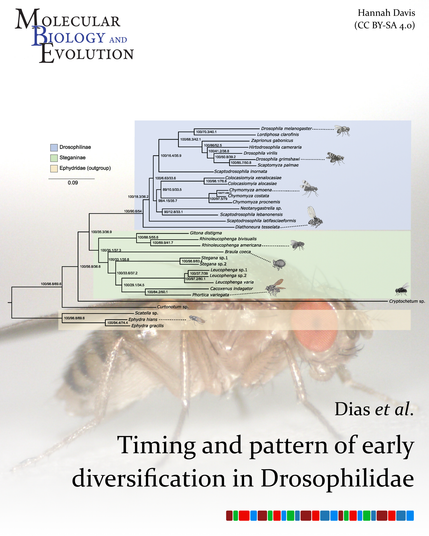
Dias et al. used genetic data from 27 Drosophilidae species and 6 outgroups to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships of fruit flies, recovering Drosophilidae as nonmonophyletic, underscoring the need for taxonomic revision.
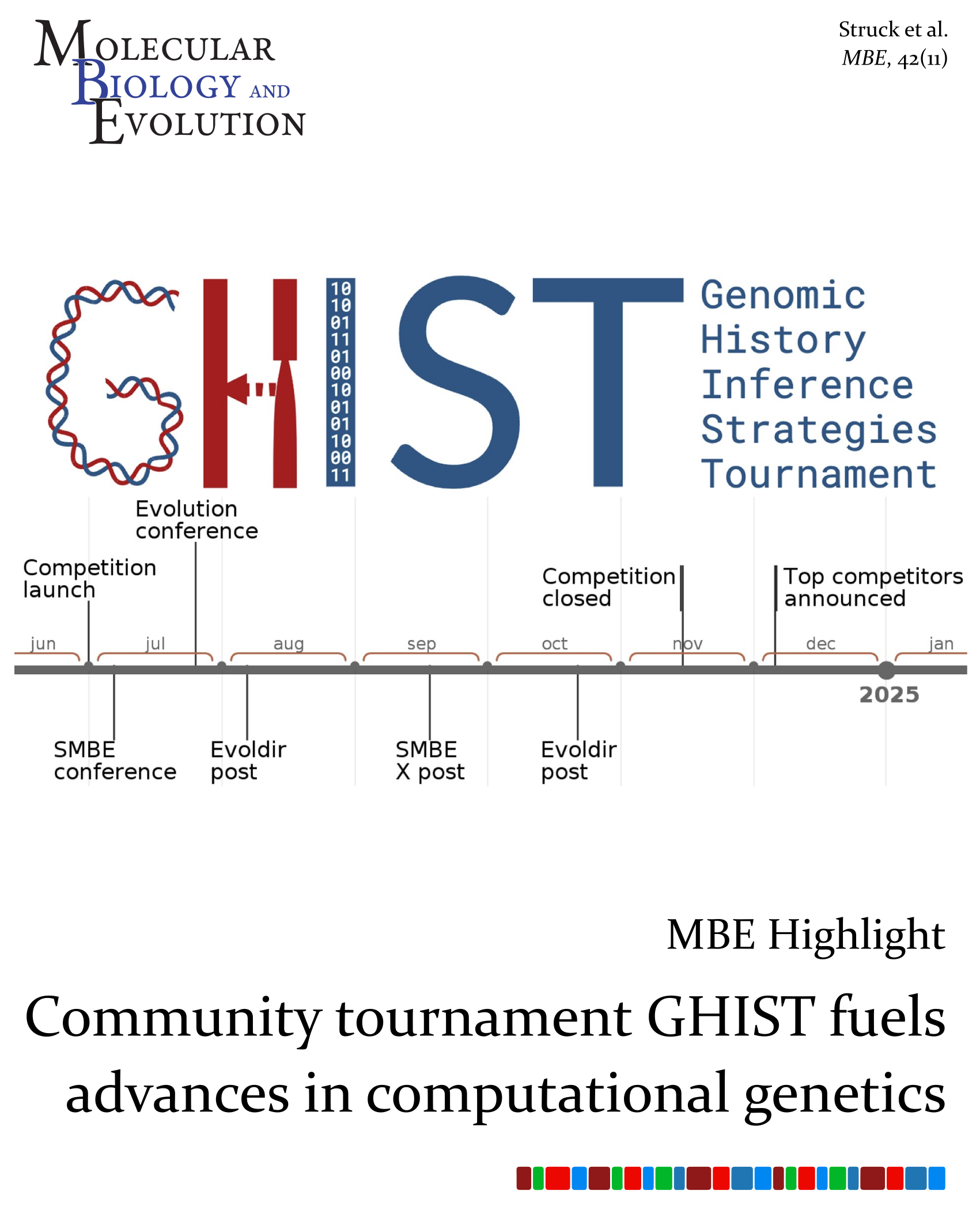
Our recent article on GHIST, the community competition to benchmark methods in genomic history inference, is the focus of this month's Highlight.
Highlight: Community Tournament GHIST Fuels Advances in Computational Genetics