Will Rio Tinto leave Madagascar a toxic legacy?
The beauty of slag
Involution and Overcapacity in China: Why Policy Fixes Fall Short | Research

Involution and Overcapacity in China: Why Policy Fixes Fall Short | Research - SDF Chatter
cross-posted from: https://lemmy.sdf.org/post/50181764 [https://lemmy.sdf.org/post/50181764] > Archived [https://web.archive.org/web/20260203052402/https://www.mjemcgill.com/articles/qerdb7p438okvgguuc9b0m0zpuckdo] > > A new term has entered the lexicon of Chinese economic analysis: involution. In Chinese, this term translates to “nei-juan”, a concept that refers to a state of “excessive and self-defeating competition among Chinese companies for limited resources and opportunities”. In this situation, intensifying effort yields diminishing returns for all participants […] This phenomenon is best captured with a theatre metaphor: in a crowded theatre, one person stands to get a better view, forcing everyone else to stand as well. Ultimately, no one’s view improves, but all are exhausted from the extra effort. > > […] > > China’s involution issue is … a structural outcome [China’s] supply-side, investment-driven model [that] systematically suppresses household income to subsidize production and leads to chronic overcapacity and destructive competition. > > […] > > The trigger was the collapse of China’s real estate sector in 2021–2022. As property developers cut investment sharply, Beijing faced a serious threat to GDP growth. Because the growth model could not tolerate a decline in investment, the state redirected capital away from real estate and toward manufacturing. This shift was politically necessary to stabilize headline growth, but it was not driven by market demand. > > […] > > [Chinese] provincial and municipal governments, under pressure to meet [Beijing’s] growth targets, offered subsidies, cheap land, tax exemptions, and financing to attract investment. This led to duplicated projects and rapid oversupply. > > […] > > The surge in supply collided with structurally weak [domesstic] demand. Consumer confidence deteriorated after 2020 due to job insecurity, falling property values, and rising precautionary savings. The same growth model that fuels overcapacity also depresses consumption by transferring income from households to producers. A limited social safety net further encourages precautionary saving, reducing the effectiveness of short-term consumption subsidies. > > […] > > The polysilicon industry, a key upstream input for solar panel manufacturing, illustrates the scale of the problem. After the property collapse, in less than four years, the top four Chinese producers managed to add the capacity equal to two-thirds of the total global capacity … It puts China as world-leading in the industry, supplying about 95% of the world’s polysilicon supply. The problem is that this is roughly double the global demand. This overload of supply drove capacity utilization below 40% in 2025, forcing producers to sell panels at prices below their variable costs. > > […] > > Beijing’s “anti-involution” campaign represents a serious attempt to curb the most damaging effects of excessive competition. Measures include revisions to the Pricing Law, coordinated production cuts, and sector-specific interventions such as plans to retire excess polysilicon capacity … However, these policies treat the symptoms rather than the cause. They reduce capacity in one sector without changing growth incentives, simply shifting overinvestment elsewhere. Indeed, while investment slows in EVs and solar, capacity expansion is accelerating in petrochemicals, another sector already facing involution. > > […] > > Two reforms are essential [in China]: strengthening domestic demand and accepting lower investment-led growth … The supply-side reforms must be paired with strong fiscal support for households. In a liquidity-trap environment, fiscal policy, not monetary easing, must play the central role in restoring confidence and consumption. > > […] > > In parallel, China must reduce its reliance on manufacturing and infrastructure as primary growth engines. This would require Xi Jinping to confront an uncomfortable political trade-off: accepting lower GDP growth targets in order to pivot the economy toward services, consumption, and household income growth. > > […]
That gas helps shape the atmosphere that protects life on Earth.
Why scientists are watching the polar sky so closely 👇
https://alaskaheadlineliving.com/polarnox-rocket-launches-from-alaska-to-track-mysterious-upper-atmosphere-gas/
#PolarNOx #AuroraBorealis #AlaskaScience #SpaceCurious #NASA #WhyItMatters #PokerFlatsResearchRange #ScottBailey #Science #EarthScience #Alaska #rocket
#EarthScience #Paleoclimatology #Geochemistry #sflorg
https://www.sflorg.com/2026/02/es02022601.html
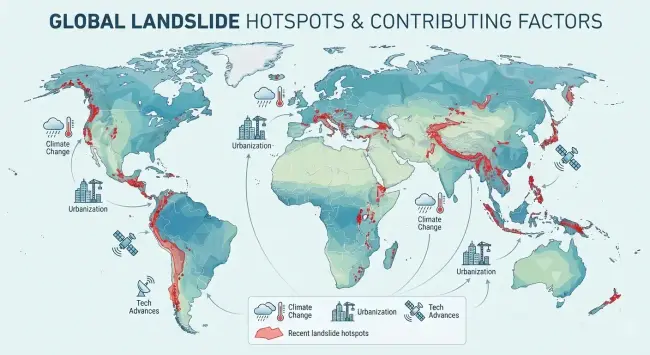
The geological complexity index (GCI) revolutionizes landslide risk modeling by integrating tectonic, lithologic, structural, and seismicity factors. As shown in Zhang's study, it boosts predictive accuracy over traditional methods, enhancing terrain analysis and enabling better hazard zoning for safer communities worldwide. #Geology #DisasterRiskManagement #LandslidePrediction #EarthScience
Earth is 'missing' lighter ele...
Tanzania is losing fertile land to soil erosion: what’s happening and what can be done
Tanzania is losing fertile land to soil erosion: what’s happening and what can be done - SLRPNK
cross-posted from: https://slrpnk.net/post/33595164 [https://slrpnk.net/post/33595164] > > Indigenous land conservation practices such as seasonal grazing and shifting cultivation recognised this vulnerability by allowing the vegetation and soil to recover. However, these were gradually eroded by colonial and postcolonial governance, which prioritised formal land tenure and permanent settlement but paid little attention to soil productivity and protection from erosion. > > > Ultimately, erosion control cannot be treated as a solely environmental problem [https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aaea8b].
Earthquake sensors buried in t...
#Meteorology #EarthScience #sflorg
https://www.sflorg.com/2026/02/cat0201203.html