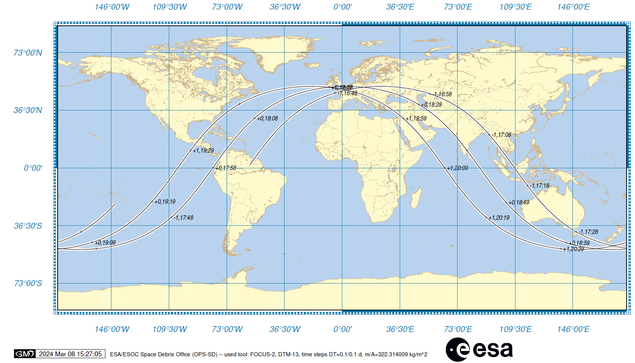
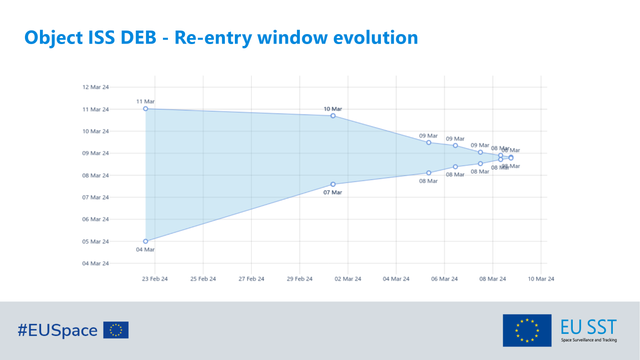
#SpaceDebris 🗑️ reentry 🔥 expected between approximately 15:35 CET and 22:25 CET on 📆 8 March https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/Space_Debris/Reentry_of_International_Space_Station_ISS_batteries_into_Earth_s_atmosphere
"If it is a human-made #SpaceObject which was launched into space 🌌 by another country, which caused damage 💥 on #Earth, that country would be absolutely liable to the homeowner 🏡 for the damage caused." https://arstechnica.com/space/2024/04/trash-from-the-international-space-station-may-have-hit-a-house-in-florida/
A month later, #NASA released a public statement taking responsibility. “The hardware was expected to fully burn up during entry through Earth’s atmosphere” https://www.latimes.com/california/story/2024-04-16/nasa-says-space-junk-that-crashed-into-florida-home-was-from-iss
#NASA incorrectly believed the batteries would completely burn up. There have been some close calls : a piece of the doomed #SpaceShuttle #Columbia crashing into a Texas dentist's office in 📆 2003, large wreckage from a Chinese 🇨🇳 #LongMarch 5B rocket damaging a village in the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire 🇨🇮, a spate of trunk debris from #SpaceX #CrewDragon missions that have landed in the United States 🇺🇸, Australia 🇦🇺, and elsewhere. https://arstechnica.com/space/2024/06/family-whose-roof-was-damaged-by-space-debris-files-claims-against-nasa/
Ariane 5 upper stages are located mainly in #GTO & just a small delta-v (1,6km/s) is left to reach the #Moon 🌙. Since the debris 🗑️ is picked up in orbit, small propulsion units are sufficient for the remaining transport to the moon. More than 150 tons of #aluminum can be regained ♻️ from #Ariane5 upper stages alone. This saves more than €50 billions 💰 of tax money in transportation costs compared to #SLS or #Ariane6 launchers. https://activities.esa.int/4000132842
A collection of academics from #universities around the world 🌏 propose turning the potential catastrophe into a resource. By 📆 2050, #GatewayEarth – a fully operational #SpaceStation with a facility to recycle ♻️ old #satellites 🛰️ and other junk – could be up and running. https://theconversation.com/space-junk-a-recycling-station-could-be-cleaning-up-in-earth-orbit-by-2050-119787
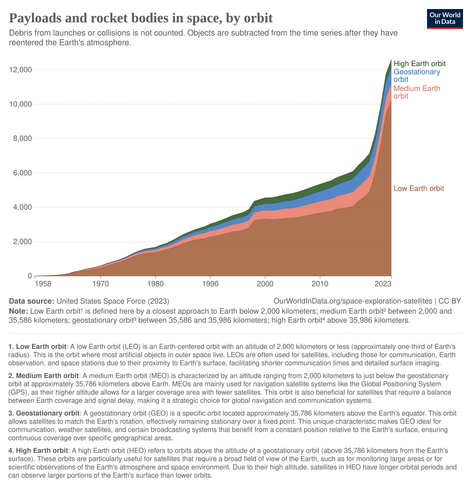
Objects in #LEO
📆 2013 : 3,890
📆 2023 : 10,225
https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/space-objects-by-orbit
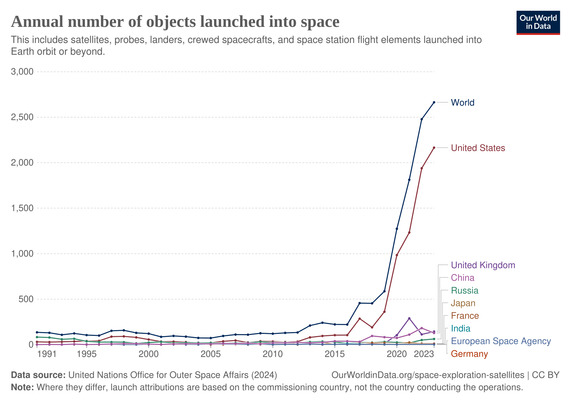
Around 100 nations are involved in varying levels of #space activity. Since the 1950s, almost 20,000 #satellites 🛰️ have been launched into Earth’s orbit. These satellites bring immense benefits to #society, from monitoring ecosystems and supporting global #communications, to facilitating services such as satellite #television and contactless bank card payments. However,...https://www.plymouth.ac.uk/news/a-sustainable-development-goal-for-space
Uncontrolled reentries of space objects create a collision 💥 risk with aircraft ✈️ in flight. The highest-density regions have a 0.8% chance per year of being affected. This rate rises to 26% 📊 for larger areas of #airspace, such as that found in the #US 🇺🇸 , #Europe 🇪🇺, or around major cities in the #AsiaPacific 🇸🇬🇭🇰 🇹🇭🇨🇳 🇦🇺 region. The collision risk could be mitigated if controlled reentries into the ocean were required for all missions. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-84001-2
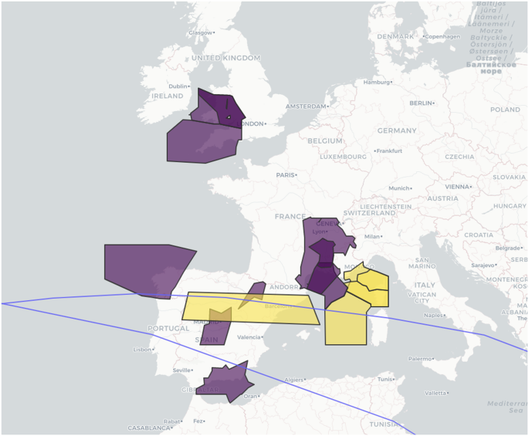
Airspace closures due to reentering space objects - Scientific Reports
Uncontrolled reentries of space objects create a collision risk with aircraft in flight. While the probability of a strike is low, the consequences could be catastrophic. Moreover, the risk is rising due to increases in both reentries and flights. In response, national authorities may choose to preemptively close airspace during reentry events; some have already done so. We determine the probability for a rocket body reentry within airspace over a range of air traffic densities. The highest-density regions, around major airports, have a 0.8% chance per year of being affected by an uncontrolled reentry. This rate rises to 26% for larger but still busy areas of airspace, such as that found in the northeastern United States, northern Europe, or around major cities in the Asia-Pacific region. For a given reentry, the collision risk in the underlying airspace increases with the air traffic density. However, the economic consequences of flight delays also increase should that airspace be closed. This situation puts national authorities in a dilemma—to close airspace or not—with safety and economic implications either way. The collision risk could be mitigated if controlled reentries into the ocean were required for all missions. However, over 2300 rocket bodies are already in orbit and will eventually reenter in an uncontrolled manner. Airspace authorities will face the challenge of uncontrolled reentries for decades to come.
We need #spacecraft that can approach ageing #satellites 🛰️ and dock with them, using #robots to repair 🔧, refuel ⛽ and upgrade them. We’ll also need a way to reuse and recycle ♻️ satellites when their working lives are over. Different types of trash 🗑️ require different removal techniques, with many ideas coming from the #fishing 🎣 industry https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-space-junk-crisis-needs-a-recycling-revolution/
🇨🇳 #Shijian25 is expected to use its robotic arms to latch onto #Shijian21 and replenish its fuel ⛽. The latter used up much of its propellant in 2022 while towing a defunct #BeiDou navigation satellite 🛰️ into a higher graveyard orbit. @planet4589 said the behaviour of the #American 🇺🇸 satellites was highly uncommon. https://www.scmp.com/news/china/science/article/3314364/chinas-landmark-orbital-refuelling-mission-why-2-us-spy-satellites-hover-nearby
With #ESA launching a third initiative in less than a year, it’s clear that in-orbit life extension 🔧⛽ is a priority for the agency https://europeanspaceflight.com/esa-to-launch-in-orbit-refuelling-demonstration-mission