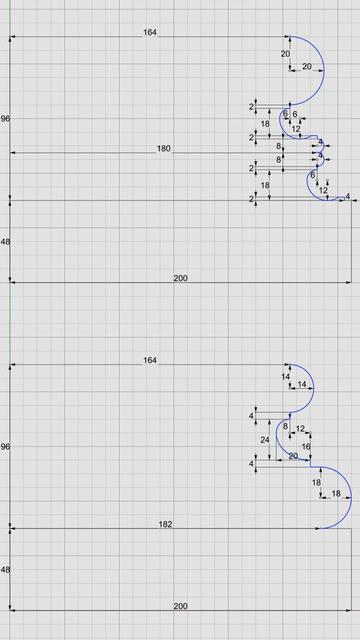
Both #Vignola base and #Attic base have the same square footprint of 400 units x 400 units. The #plinth for both is 48 units (6 parts, or µ/3) tall, and the total height for both is 144 units (18 parts, or exactly µ). As such, they are easily interchangeable.
In the Vignola variant, we start at the plinth with a #fillet 2 units tall and a classic #scotia 18 units tall gouging out part of the fillet.
Then there is another fillet 2 units tall, followed by two #reeds, each 8 units tall, followed by another classic scotia as described above.
This is followed by yet another fillet 2 units tall and topped off with a #torus 40 units tall. A Torus is the same as a reed, except larger. When we reach the neck of the shaft, we will see another molding called #Astragal which has the same profile as reed and torus, but sits in the middle in size. Think of reed, astragal, and torus as small, medium, and large of the same profile.
The modern Attic variant is more elegant with fewer moldings. It also gives the impression of more heft for more stately columns. It starts at the plinth with a torus 36 units tall, followed by a fillet 4 units tall, followed by a modern scotia 24 units tall, followed by another fillet 4 units tall, and topped off with another torus 28 units tall.
As in the construction of #IonicEntablature [https://pixelfed.social/p/Splines/791013152244518907], split the construction of the #columnBase into two steps.
Just as we extruded #dentils separately, we extrude the plinth separately. First draw a square 400x400 in the top view. Then extrude the square 48 units in the front view.
For the rest of the base, we need a new 3D operation — #revolve around an axis. Instead of extruding the #primaryProfileCurve, we revolve it around the #columnAxis, and cap the #planarHoles on both ends before performing a #booleanUnion with the plinth. Finally check edges of the solid for #nakedEdges and #nonManifoldEdges.
Splines (@Splines@pixelfed.social)
This sketch shows the arrangement of #dentils in the classic variation of the #IonicEntablature. It shows the full layout, but most of the top is obscured by the top portion of the #cornice. Only the outside square shapes are actually visible. Each #dentil has a square "footprint" that is 4 parts by 4 parts (32*32 units) and is 6 parts (48 units) tall. The spacing between each dentil is 2 parts (16 units). Dentils project 4 parts (or 32 units) from the face of the #fascia on which they rest. Each face of the fascia has 7 dentils with the middle dentil laterally centered and directly in front of the column axis. The 2 side dentils are on side faces, and that is apparent in the darker shading in the sketch at https://pixelfed.social/i/web/post/790782316675150160. Take the time to reconcile this with the numbers listed in #Scarlata's #PracticalArchitecture. The 3D reconstruction from the #primaryProfileCurves is very similar to that of the #IonicPedestal, with #extrusion, #mitering, #joining, and #capping planar holes as described in https://pixelfed.social/i/web/post/790645054230337543 — just set the dentils aside, for now. Once you have capped the #planarHoles to get a solid, analyze the edges of the solid in the #CAD program for #nakedEdges and #nonManifoldEdges. Then, extrude the dentils outline (in the top view) to a height of 48 units (in the front view). Now perform a #booleanUnion of the two solid shapes to get the complete #entablature. Finally, check the edges of the solid in the #CAD program AGAIN for #nakedEdges and #nonManifoldEdges. With this, we have finished two of the three main components of the #IonicOrder. There's a modern version of the Ionic entablature with #modillions, which I will describe later. Next, we move on to the biggest, most conspicuous part of the order — the #IonicColumn.