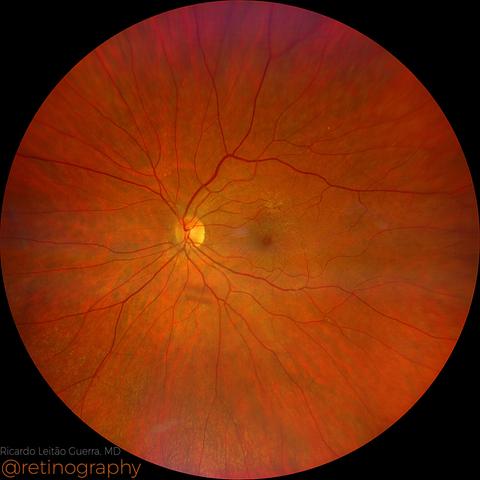
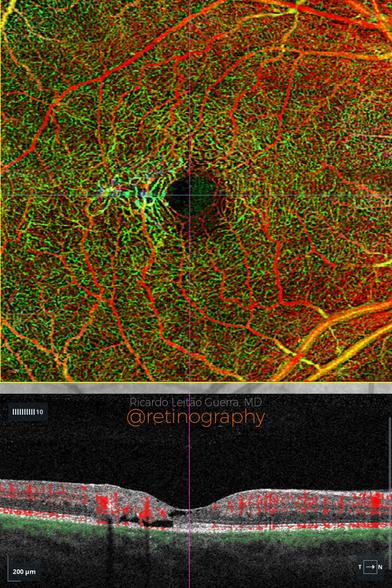
Macular pseudohole
Macular pseudohole is characterized by a steepened foveal contour without a full-thickness defect. On Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), it shows a narrow, deep foveal pit with intact outer retinal layers, typically caused by a contractile epiretinal membrane (ERM). Differentiating it from a true macular hole is essential, as visual prognosis and management differ significantly. #MacularPseudohole #ERM #OCT #FovealContour #RetinaImaging #retina…