https://www.livescience.com/space/space-exploration/china-is-building-a-constellation-of-ai-supercomputers-in-space-and-just-launched-the-first-pieces
Marshall Eubanks
- 171 Followers
- 175 Following
- 3.7K Posts
https://www.livescience.com/space/space-exploration/china-is-building-a-constellation-of-ai-supercomputers-in-space-and-just-launched-the-first-pieces
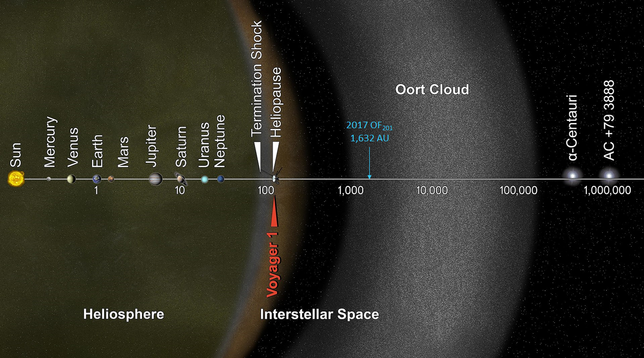
The following graphic illustrates the extent of the orbit of 2017 OF201 within the Solar system, touching the inner region of the Oort Cloud.
The Oort cloud is a vast cloud of icy planetesimals surrounding the Sun at distances ranging from 2,000 to 200,000 AU.
The NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft, launched in 1977, is currently ~167 AU from the Sun.
1 AU = mean Sun-Earth distance ~= 150 million km.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oort_cloud
https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA17046
4/n
2017 OF201 was discovered from archival data from the Dark Energy Camera Legacy Survey.
The Dark Energy Survey (DES) Collaboration is an international effort to study the properties of dark energy. The DES was conducted using the 4-metre Blanco Telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Chile from 2013 to 2019.
The survey used the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) with a wide field of view ~14x the angular size of the Moon.
https://aasnova.org/2024/10/29/testing-cosmology-with-the-dark-energy-survey-five-year-supernova-dataset/
https://www.darkenergysurvey.org/the-des-project/instrument/
3/n
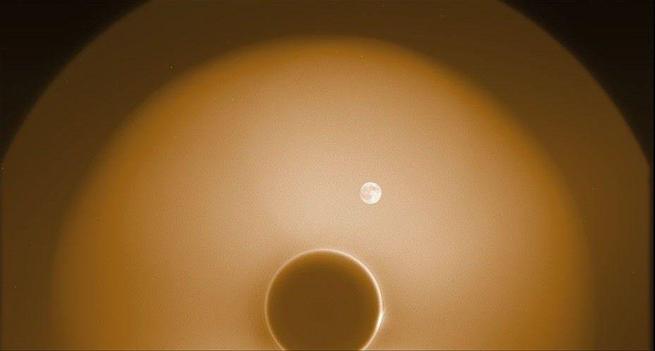
Some serendipitous space beauty to start your weekend.
NASA's new PUNCH mission, designed to study the solar wind, just took this ethereal image of the Moon passing the (blocked out) Sun. The Moon's night side is facing us, but it's beautifully lit by Earthshine.
https://science.nasa.gov/blogs/punch/2025/05/12/nasas-punch-catches-first-rainbow-and-other-new-images/ #science #art #nature
A Preliminary Search for Planets and Exozodiacal Emission Around α Centauri A with JWST/MIRI
We present F1550C (15.5 μm) coronagraphic imaging observations of the nearest solar-type star α Cen A using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI). The observations, executed in 2025 February, were compromised by having only one successful roll and degraded performance due to a position mismatch (Δr ∼ 10 mas) between α Cen A and the best-matching reference observation behind the MIRI coronagraph. We set preliminary upper limits on both the presence of a planet and an exozodiacal dust disk.
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2515-5172/add880/
welcome to the future, now your error-prone software can call the cops
(this is an Anthropic employee talking about Claude Opus 4)
One bonus of DOGE:
every time they kill something, it’s an opportunity to learn about another genuinely cool thing our federal government was once trying to do for the American people
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.15806

Discovery of a dwarf planet candidate in an extremely wide orbit: 2017 OF201
We report the discovery of a dwarf planet candidate, 2017 OF201, currently located at a distance of 90.5 au. Its orbit is extremely wide and extends to the inner Oort cloud, with a semi-major axis of 838 au and a perihelion of 44.9 au precisely determined from 19 observations over seven years. Assuming a typical albedo of 0.15, we estimate a diameter about 700 km, making it the second-largest known object in this dynamical population and a likely dwarf planet. Its high eccentricity suggests that it is part of a broader, unseen population of similar objects totaling about 1 % of Earth's mass. Notably, the orbit of 2017 OF201 lies well outside the clustering of longitude of perihelion observed in extreme trans-Neptunian objects, which has been proposed as dynamical evidence for a distant, undetected planet.
New Large Sednoid 2017 OF201
https://minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K25/K25K47.html
a=880au, e=0.94, now r= 90au
H = 3.46
Estimated Diameter =
8.5e+2 km
for an albedo of 0.1
from findorb
P period 24260 years
H 3.46
q = 44.6520493 +/- 0.0271 Q = 1631.44568 +/- 42.4 (AU)
The Event Horizon Telescope is a worldwide network of radio telescopes that gave us the first images of a black hole's event horizon. Researchers have demonstrated a new technology called "frequency phase transfer (FPT)" which will make the network even more sensitive and capture data at multiple wavelengths which can enhance one another. With this demonstration complete, future observations by the EHT could make multi-color images of a black hole.
Astronomers take the first step towards multi-color black hole observations with the Event Horizon Telescope | Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian
Cambridge, MA - An international team of astronomers has successfully demonstrated a new technique to observe especially faint black holes by correcting for atmospheric effects on Earth. The technique, called “frequency phase transfer (FPT),” can now be implemented at observatories participating in the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT), making the global array more sensitive than ever before.