"OpenAI has announced the launch of an "agentic security researcher" that's powered by its GPT-5 large language model (LLM) and is programmed to emulate a human expert capable of scanning, understanding, and patching code.
Called Aardvark, the artificial intelligence (AI) company said the autonomous agent is designed to help developers and security teams flag and fix security vulnerabilities at scale. It's currently available in private beta.
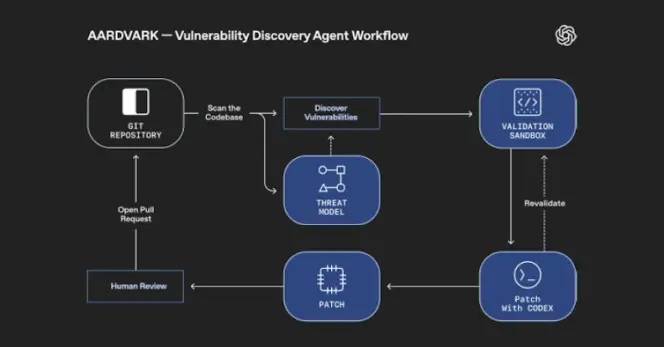
"Aardvark continuously analyzes source code repositories to identify vulnerabilities, assess exploitability, prioritize severity, and propose targeted patches," OpenAI noted.
It works by embedding itself into the software development pipeline, monitoring commits and changes to codebases, detecting security issues and how they might be exploited, and proposing fixes to address them using LLM-based reasoning and tool-use.
Powering the agent is GPT‑5, which OpenAI introduced in August 2025. The company describes it as a "smart, efficient model" that features deeper reasoning capabilities, courtesy of GPT‑5 thinking, and a "real‑time router" to decide the right model to use based on conversation type, complexity, and user intent.
Aardvark, OpenAI added, analyses a project's codebase to produce a threat model that it thinks best represents its security objectives and design. With this contextual foundation, the agent then scans its history to identify existing issues, as well as detect new ones by scrutinizing incoming changes to the repository."
https://thehackernews.com/2025/10/openai-unveils-aardvark-gpt-5-agent.html
#CyberSecurity #AI #GenerativeAI #OpenAI #Aardvark #AIAgents #LLMs #GPT5