From a Different Star: 3I/ATLA...
From a Different Star: 3I/ATLA...
Predicting Interstellar Object...
Predicting Interstellar Object Chemodynamics with Gaia
The interstellar object (ISO) population of the Milky Way is a product of its stars. However, what is in fact a complex structure in the solar neighborhood has traditionally in ISO studies been described as smoothly distributed. Using a debiased stellar population derived from the Gaia Data Release 3 stellar sample, we predict that the velocity distribution of ISOs is far more textured than a smooth Gaussian. The moving groups caused by Galactic resonances dominate the distribution. 1I/'Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov have entirely normal places within these distributions; 1I is within the noncoeval moving group that includes the Matariki (Pleiades) cluster, and 2I within the Coma Berenices moving group. We show that for the composition of planetesimals formed beyond the ice line, these velocity structures also have a chemodynamic component. This variation will be visible on the sky. We predict that this richly textured distribution will be differentiable from smooth Gaussians in samples that are within the expected discovery capacity of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory. Solar neighborhood ISOs will be of all ages and come from a dynamic mix of many different populations of stars, reflecting their origins from all around the Galactic disk.
From a Different Star: 3I/ATLA...

From a Different Star: 3I/ATLAS in the context of the Ōtautahi-Oxford interstellar object population model
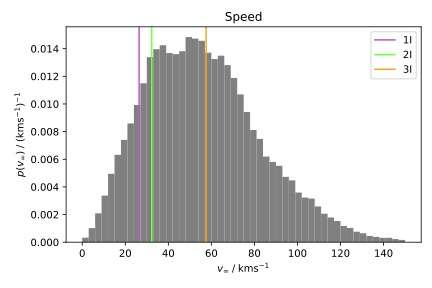
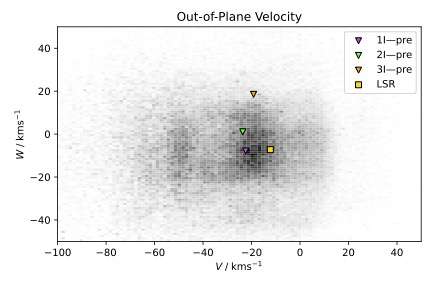
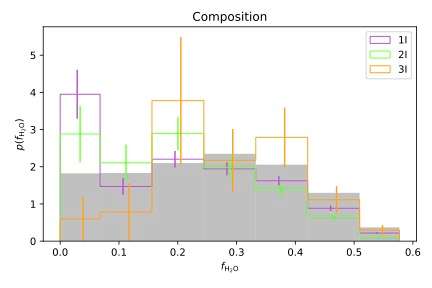
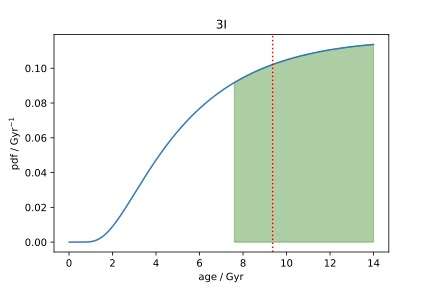
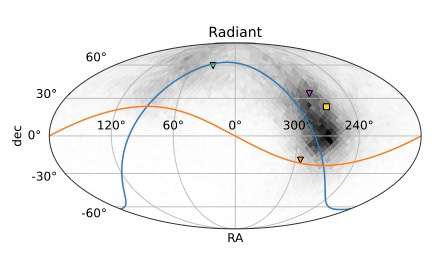
The discovery of the third interstellar object (ISO), 3I/ATLAS (`3I'), provides a rare chance to directly observe a small body from another Solar System. Studying its chemistry and dynamics will add to our understanding of how the processes of planetesimal formation and evolution happen across the Milky Way's disk, and how such objects respond to the Milky Way's potential. In this Letter, we present a first assessment of 3I in the context of the Ōtautahi-Oxford model, which uses data from Gaia in conjunction with models of protoplanetary disk chemistry and Galactic dynamics to predict the properties of the ISO population. The model shows that both the velocity and radiant of 3I are within the expected range. Its velocity suggests an origin within the Milky Way's thick disk, making it the first ISO from this population, and predicts a high water mass fraction, which may become observable shortly. We also conclude that it is very unlikely that 3I shares an origin with either of the previous two interstellar object detections.