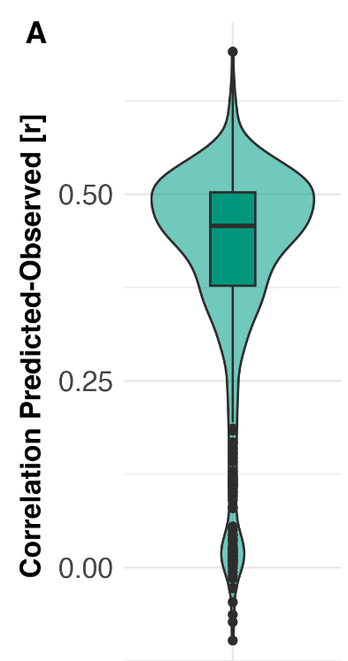
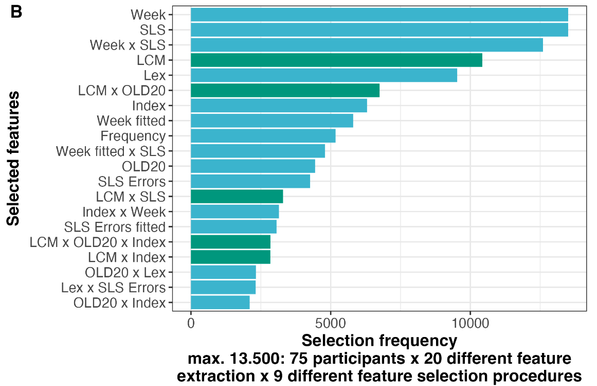
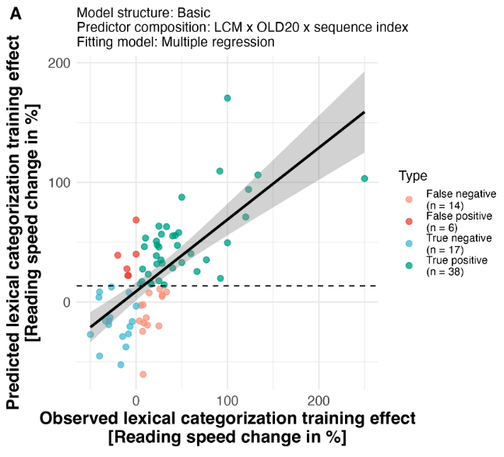
🚨🚨NEW PREPRINT 🚨🚨 "Investigating lexical categorization in visual word recognition based on a joint diagnostic and training approach for language learners." https://psyarxiv.com/rs6gy/
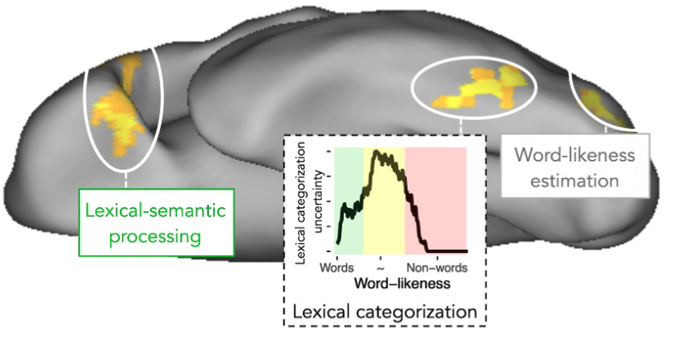
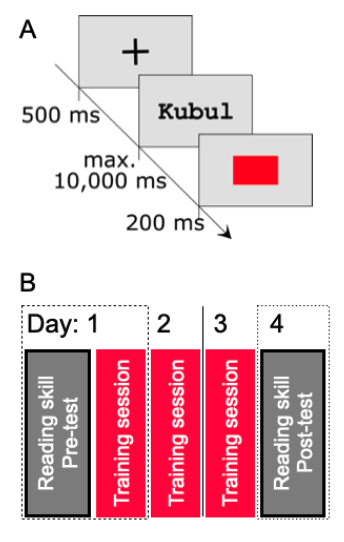
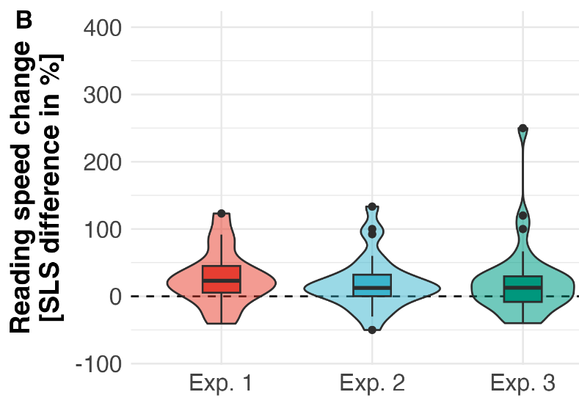
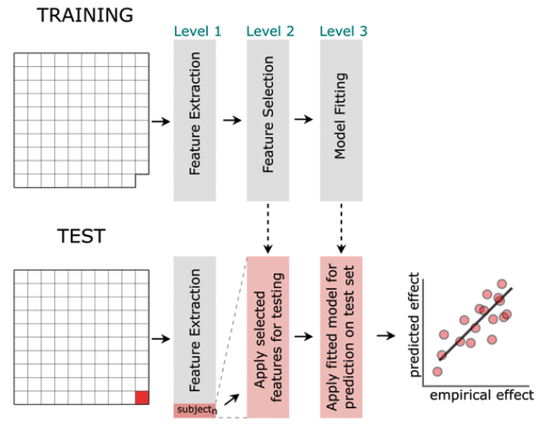
We designed a training program including a machine learning-based diagnostic approach to train lexical categorization optimally, i.e., the process most likely implemented in the visual word form area (https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009995). 1/N
We designed a training program including a machine learning-based diagnostic approach to train lexical categorization optimally, i.e., the process most likely implemented in the visual word form area (https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009995). 1/N